
Frozin sources a wide range of beef cuts and veal cuts from the best Halal suppliers around the world. Send us an inquiry today by filling out the form on ourCONTACT page.
Beef Topside

The topside is the inner thigh muscle, situated on the inside of the back leg, near the hip bone. It is removed by following the natural seam between the knuckle and the silverside.
Beef Silverside

The Silverside is prepared from the hindquarter and comes from the outside of the rear leg. It sits between the knuckle and the topside. It gets its name because of the silver wall of sinew on the side of the cut; this is a long fibrous “skin” of connective tissue, which has to be removed as it is too tough to eat.
Thick flank

The flank steak is an extremely versatile cut of meat. This cut is processed practically free of fat and connective tissue, so very little, if any, trimming is required. Although it is a cut with quite a lot of nerves, the skirt is gelatinous and very tasty.
Beef Tenderloin

The tenderloin is one of the least used muscles on the animal, making it an incredibly tender piece of meat. This is one of the most valued cuts, which is located on the inner side of the lower back. It can be divided into top, bottom and tip.
Rump

The rump, a five-muscled primal sitting in between the sirloin and the topside, is cut from the hindquarter and is a boneless piece that covers the hip bone of the animal. It is a great full-flavored and the grains of each muscle that make up the rump run in different directions and have different textures and levels of tenderness. The rump is a juicy, tender cut that is low in fat and heart-shaped.
Strip Loin

The striploin sits on the lower part of the animal’s backbone, from the bottom of the cube roll to the top of the sirloin. The back of the loin is also lean, juicy, and tender. While the prime ribs are lengths of the long ribs, the striploin contains the short ribs, but their culinary uses are the same.
Buffalo Trimming

BRAIN
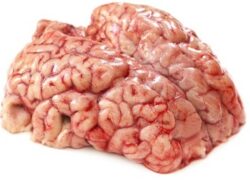
contains omega 3 fatty acids and nutrients. The latter include phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylserine, which are good for the nervous system.
LIVER

The liver is the most nutrient-dense organ meat, and it is a powerful source of vitamin A. Vitamin A is beneficial for eye health and for reducing diseases that cause inflammation, including everything from Alzheimer’s disease to arthritis. The liver also contains folic acid, iron, chromium, copper, and zinc and is known to be particularly good for the heart and for increasing hemoglobin level in the blood.
HEART
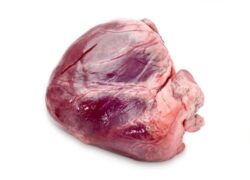
The heart is rich in folate, iron, zinc, and selenium. It is also a great source of vitamins B2, B6, and B12, all three of which are in a group known as B-complex vitamins. B vitamins found in organ meats have a cardioprotective effect, meaning they protect against heart disease. B vitamins are also associated with maintaining healthy blood pressure, reducing high cholesterol, and forming healthy blood vessels.
KIDNEY

The Kidney Rich in nutrients and proteins, kidney meat contains omega 3 fatty acids. It is also known to contain anti-inflammatory properties and to be good for the heart.
Veal Leg

veal leg hind saddle The choice meat in the leg is often sliced into thin cutlets to be used for veal scaloppini, schnitzels, and escalopes. You can also buy larger cuts for roasting or braising.
Bobby Veal

Bobby veal Meat of young calf (Bos taurus) 2½–3 months old. A 150‐g portion is a rich source of protein, niacin, iron, vitamin B12, and selenium; a good source of vitamins B1, B2, B6, and zinc; a source of copper; contains about 15 g of fat of which one‐third is saturated; supplies 350 kcal (1470 kJ).
Veal Tenderloin

Veal tenderloins are similar to beef tenderloins in that they are one of the animal’s most tender sections, but are milder in flavor.


